Aneurin Hughes, Cardno, asked me this question at AM Peak last week.
It got me thinking and I realised that I never had an expectation, or long term vision, and I still haven’t. If it was hard to see the future back then, it certainly hasn’t got any easier now.
And yet, without any formal long-term planning, we have made incredible strides. Which is what makes looking back to where we started so fascinating.
I had certain things I believed in – that we needed to know WHAT we were doing, WHY we were doing it, and how much it was COSTING us – for these were necessary to make sensible decisions. These were basic so I was surprised to find so little attention to them when it came to infrastructure.
Today these same questions still apply – but now we are able to tackle them in far greater depth and complexity. And I think that ability (and the desire to apply it) is what has changed the most over the last almost four decades. Once we thought of WHAT in simplistic physical and immediate terms, now it embraces the impact we have having on the environment and on society now and into the future. The WHY question which used to be ‘what’s in it for us’ where the ‘us’ was the supply organisation, now looks further and is forcing us to have a greater understanding of the role of infrastructure beyond its mere ‘job creation’ aspects, to consider the myriad ways in which infrastructure interacts with the way we ‘live, work and play’.
The question of COSTS is perhaps the most controversial one we are dealing with today. Initially we knew almost nothing and a lot of the early development of AM focused on understanding this better. At first we just looked to the financial cost to the supply organisation and ignored those external costs that fell on users, or on the community – both now and future. These are now, at least, being discussed, but we still have some way to go before we make the necessary institutional changes that will enable the issues being discussed to be implemented. In the meantime, so many incentives remain counter-productive.
So my answer to Aneurin was, of course, ‘No’, because I had no theoretical long term vision. Instead my approach to AM was more pragmatic, more incremental, I just tackled the next problem that I could see.
QUESTION: Do you have a vision? If so, what are the next steps on the way to achieving your vision?
We have uploaded Chapter Two of ‘Asset Management as a Quest’ today.
It is now almost 40 years since Asset Management started. To celebrate, Talking Infrastructure is producing a history of the development of our discipline, now a recognised industry and moreover one for which there is excess demand.
‘Asset Management as a Quest’ is the first in this four volume series and it covers the period from 1984 to 1993. While future volumes, each covering one decade, will call on the ideas, experience and stories from many leading practioners, the first volume is told by Dr Penny Burns, and it is the story through her eyes.
Part One, consisting of 4 chapters, was first published in July 2021. It is now revised and we will be presenting the whole volume, all 20 chapters, one chapter at a time each fortnight. You can find the first chapter, ‘How Asset Management Began’ here.
Information on how you can be part of Volumes 2-4 coming shortly – so, if you have not yet joined Talking Infrastructure (it’s free!) do so, and you will be the first to be advised.

A new world, new questions
Today is the 5th Anniversary of Talking Infrastructure. It was created in July 2016 to consider the new world we are now in – and the new questions this world and its challenges requires.
It is now massively evident that whereas a focus on competition to secure the success of individuals and individual companies has generated much that we enjoy today, it has also generated serious problems, of which climate change and social inequity are just the most visible.
Infrastructure – problem or solution?
While we may be reluctant to admit it – infrastructure has been a large part of the problem! Every infrastructure does considerable environmental damage. And not every infrastructure generates commensurate community benefit. A few months ago, I said’ Goodbye to our Talking Infrastructure Guy’, – and explained what was wrong with our current attitudes to infrastructure. Today he is formally replaced as our icon.
So welcome our new icon – the Australian platypus – symbolic of the collaboration we so badly need. The platypus was originally regarded as a joke, for it was considered an impossibility, being so many different animals all in one. And this version of the platypus reflecting our aboriginal culture is particularly appropriate. The Australian aboriginals are the oldest civilisation in the world sustaining the land for over 50,000 years. That’s resilience! And they have done it by a focus on community, rather than self, and a veneration for the land that supports us.
If we want a future that will support our children and theirs, we need to embed these iconic qualities of community, resilience, and sustainability in all of our decisions – and especially in our long term infrastructure decisions – from new and renewal to ongoing maintenance and even to eventual withdrawal.
What questions do we now need to ask ourselves in order to secure this future?
Hint: They are not the questions that we started with in asset management and which I discuss in volume 1 of our series, The Story of Asset Management. Consider the ten questions I pursued in the first 10 years (1984-1993) which you can find here Or, to see the questions in context, see “Asset Management as a Quest – contents”.
After you read these questions, consider to what extent we have already solved (or at least know the solution to). Then ask yourself what the questions for the next ten years should be.
And, if you would like to see how I came up with these questions to start with, you may enjoy the first chapter of “Asset Management as a Quest” which you can find here. The full volume will be available in the New Year.
What do you consider the most important questions? Please add them below.

Our latest project! The Story of Asset Management
I hope you have been enjoying Ruth’s platypus posts on our blog as much as I have – and reflecting on the interesting and critical question she has been exploring, namely, what does it mean to be an asset manager?
This is not a simple question to answer. Which is why it needs thinking about. I have been doing much thinking about it over the past few months as I have worked on the first volume of Talking Infrastructure’s 4 volume narrative, ‘The Story of Asset Management’.
Each of the four volumes covers one decade, starting in 1984, to be finished by the end of 2023. Each volume has its own theme:
- Asset Management as a Quest. 1984-1993
- Asset Management as an Opportunity. 1994-2003
- Asset Management as a Discipline. 2004-2013
- Asset Management as a Business (and beyond?) 2014-2023
Team work
As Ruth has shown in her recent posts, Asset Management needs a team.
Our story of asset management is the story of how those teams developed, how they came together over key ideas, how they fought with each other and supported each other – and became the very special kind of multi-disciplinary, multi-national tribe we are all part of today.
You are wanted!
If you would like to be part of the story we tell, become a member of Talking Infrastructure today and we will let you know more.

Dreamstime.com/ 187958062 © Meg Forbes
The world of infrastructure Asset Management has had the benefit of an evolutionary model for several years: the ‘Waves’ of Penny Burns, to make sense of how organisations seem to have to go through a period of focus on basic information (Wave 1, Asset Inventory) before they really look at how to use it to make better decisions, to start optimising (Wave 2, Strategic Asset Management).
Before that, I confess, I struggled to express what was going on: how could people get stuck in data and databases? I don’t know that I fully understand, still, but I least I recognise it now – that having a list of all your assets, simple facts like install date and location, and a big dumb database to put it all in preoccupied so many of us for so long.
Penny herself seems not to have spent too much time worrying about this, but always had a vision way beyond it. She assumed we would have a grip on lifecycle costs, thinking longer term, and planning ahead, and get down to acting smarter on our asset decisions.
And now, as we work together to capture our collective history and development, we are really looking forward to the next Wave. To really so much better infrastructure decision making that is fit for purpose, through the rest of this turbulent century.
Look out for celebrating our history on July 29th!

Dreamstime.com/ 191317844 © Lefteris Papaulakis
It’s always an interesting question: why do things arise when and where they do? Why Asset Management in Australia in the 1980s, when plenty of other useful asset ideas came from other places and times – reliability engineering in US commercial airlines post-war, for instance?
And when I explain where much best practice comes from, why is New Zealand such a paragon? There are very good reasons, when you ask about the when and the where.
There is something about fundamental ideas that makes understanding the specifics important. An approach that seems like such a good idea as Asset Management – why wasn’t it more obvious, earlier, to more people? A fabulous clue as to how what seems like an obviously sensible mindset, required something major to shift. A chink in older assumptions, even culture, that let someone, something start to question, to let a new light in.
I suspect a lot of us struggle about why people resist what seems backed by logic, evidence and good sense. But I don’t want us to go down the deep, dangerous rabbit hole that is conventional economics, making a simplifying assumption that people are ‘rational’ the way they define it – a definition which doesn’t really care why people do what they do, or how what seems ‘obvious’ in one situation doesn’t work in another, or anywhere.
And that is partly why I love physical infrastructure. One size really doesn’t fit all* – a good strategy for one kind of asset would be barking wrong for another, and even for an identical asset in a different context. And it all depends on what you are trying to achieve, specifically.
Physical assets are the opposite of idealised generalisations. Yes, there are generally good questions; but not universal good answers, at least not in my experience.
Infrastructure Asset Management is the epitome of the full appreciation of time and place.
Watch here for the publication of the first part of Penny Burns’ history of Asset Management, from its beginnings in South Australia….
*Thanks to a Bay Area shoestore billboard, and Robyn Briggs ex Pacific Gas & Electric, for this!

“The farther back you can look, the farther forward you are likely to see” Winston Churchill
Until around 1996 the terms ‘Asset Management’ and ‘Strategic Asset Management’ were practically synonymous. But with the increasing popularity of the term ‘Asset Management’ to describe a wide variety of activities, as described in Pt 1, there was a need for a term that could differentiate decision making from the doing so, in January 1999, when the Asset Management Quarterly became fortnightly and thus needed a name change, I chose “Strategic Asset Management”, popularly known as SAM.
This was to stress that Asset Management wasn’t maintenance and reliability, or capital acquisition, or Treasury asset sales or many of the other associated activities, but rather what later became known (in ISO 55,000) as ‘the alignment of asset activities with the goals and objecitves of the organisation’
The first issue of SAM, January 1999, explained the name change, and in doing so, focused on what differentiates asset management from what went before.
“The real key to being strategic is where you focus your attention. If you focus on what you are doing you are carrying out an operational task; if you focus on how you are doing it, seeking to ‘tweak it’ or do it better, then you are engaged in a tactical activity. Both of these are necessary and important. However, they are not strategic. The strategic task is the one that focuses on the outcome, or the purpose….What constitutes a ‘better’ outcome, however, is not for the maintenance manager to decide. A ‘better’ outcome is one that moves the agency in the direction of its strategic vision.
By way of illustration, take the construction of a new hospital. If the questions you are asking yourself are ‘what is the purpose of this new hospital; what needs are we providing for, should we be providing them or should they be provided by others, or should they not be provided at all; is a new hospital required or are there better means?’, then you are focussing on the outcomes – ie being strategic.
Asking yourself ‘should this construction be carried out as a ‘design-construct’, ‘build-own-operate’ or some other form of contract’ is asking tactical questions. If you ask ‘how do I ensure this construction comes in within time and budget and is of the right quality’ then you are engaged in an operational task.
Thus ‘Strategic’ is not the same as ‘Important’. ALL aspects of asset management are important.”
In January 2014, the first international standard in asset management, ISO 55,000 was launched, and with this, we came to the end of the beginning of Asset Management. No longer a novelty, a new-comer; Asset management arrived.
For What Happened Next see: AM – The third wave

In Australia, interest in asset management arose as the result of a series of eight parliamentary reports in South Australia in 1986/1987 modelling the likely cost and timing of renewing all the State’s major infrastructure assets.
The projected costs were so large that they would have absorbed the State’s total capital budget within the next 10 years if urgent action was not taken. To address this problem, the recommendations in the reports covered possible planning and accounting reforms as well as engineering and maintenance changes.
Following the Public Accounts Committee’s Reports, a major SA Government Task Force was established that reviewed, then agreed and reinforced all the ideas presented in the reports. This led to the formation of a Cabinet sub-committee to consider the issues raised, This provided high level impetus for the development of asset management.
Further support was provided by the Auditors-General who were appalled to find that no public sector department. not even the statutory authorities, had decent asset registers and they made this a requirement.
But the most significant change was that led by the Australian Accounting Standards Board. At this time the board covered accounting standards in both the private and the public sectors. The private sector used commercial standards with accrual accounting but the public sector used cash accounting. The board wanted to standardise on accrual accounting for both but was concerned about how this would be received. When it learnt that the Parliamentary Public Accounts Committee in South Australia was promoting the idea of accrual accounting to better understand and deal with infrastructure asset management, it was encouraged to push ahead. Within two years of the release of the final PAC report, the board had released Exposure Draft 50, the model of accrual accounting for local government.
The introduction of accrual accounting meant that local, state and federal government departments were required to move from their previous practice of simply recording annual cash in and cash out, to establishing balance sheets and recording, for the first time, the depreciated value of their infrastructure and other assets,
You might think that an accounting change would be of no interest to maintenance engineers. Fortunately @Roger Byrne was not your ordinary maintenance manager. He had already been in the habit of including economic and planning issues in briefing notes for his clients and he quickly seized on the opportunity this change presented for maintenance engineers.
It was these briefing notes that later provided the content for the first local government asset management manual which subsequently became the IIMM we all use today. So through top down interest and bottom up capacity building, Australia took an early lead in the development of asset management.
The Parliamentary Reports created a lot of interest Australia wide. No other state was prepared, or even able, to duplicate the research for their own constituency but all infrastructure agencies recognised that the conclusions reached applied as much to them as it did to their South Australian counterparts. The CSIRO’s Engineering and Construction division took an active interest, as did State Treasuries and the Auditors-General.
With these organisations, I continued to develop the ideas that had arisen and, after advising governments, commissions of audit, and infrastructure agencies themselves, I created ‘The Asset Management Quarterly’ publication in 1994 to share with others what I was learning. Then, in 1996, noting that lots of interesting things were being done in the name of asset management – but nothing was being documented, I launched the International Asset Management Competitions where the awards went to the best documentation of good asset management practice. They ran between 1996 and 2000 and in 1998 AMQ International launched the world’s first asset management website with information on asset management freely available to all.
The term ‘asset management’ started to become very popular and everyone wanted to get in on the act. One day, flying from Sydney to Canberra my seat companion described herself as an asset manager – on questioning it turned out that she was actually a real estate developer! Once off the plane and into a taxi, on the taxi radio I heard an advertisement for ‘asset management services’ – which turned out to be office cleaning! Yes, asset management had become the buzzword ‘de jour’.
To be continued….
A REQUEST
I am currently working on a book about our beginnings and would love to speak with anyone about their recollections pre 2014.
Please leave your name below and I will contact you.

Homo Sapiens is a pattern seeking species
it is how we advance. We seek patterns to find meaning. Me, I look for patterns in AM development. I seek the characteristics of the different stages (that I now think of as waves rather than as revolutions, as explained in the last post) and how each builds on the one before and takes us further. This helps me to see not only where we have been but also where we can go. Each wave has its own focus, viewpoint, key players and sources of support as well as constraints. Below is a table illustrating some of the characteristics of the first three waves that I see. What do you think?
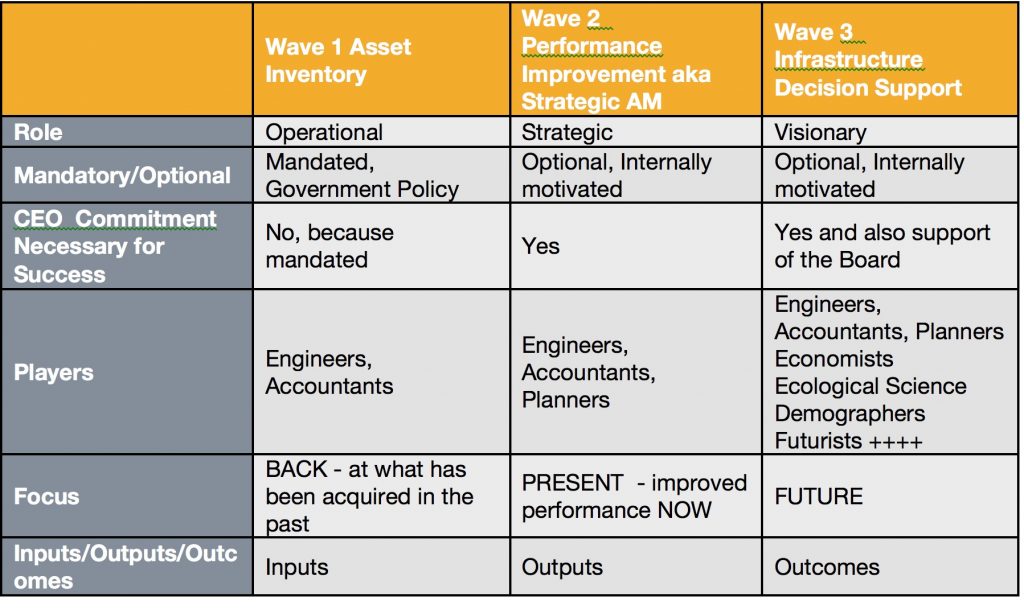
Where we have been and where we are
Waves 1 and 2 you will readily recognise, for they reflect where we have been and where we are. Wave 3 is where we need to go next. This is the visioning stage where asset management teams, use their appreciation of ‘line of sight’ or the necessity for asset actions to support organisational objectives to guide decisions on both new and existing infrastructure. This is where AM teams need to anticipate, communicate, and prepare for the inevitable shifts in attitudes, governance and demand, that are now occurring and will continue to occur as demographics, climate and technology change. Turning around large infrastructure portfolios is not an overnight task. It takes intelligent planning and communication. This is Wave 3.
Where we are going
Communication, anticipation, action. In Wave 3 AM teams help their corporate managements to explicitly recognise that the asset portfolios and management practices they have now are a reflection of the past, and that the future will be very different from the past and will involve new thinking. This may seem obvious, but it is not necessarily happening at the moment. Sometimes it seems that it is easier to assume that nothing will change very quickly so we can continue doing what we have always done. And sometimes the lure of the new and shiny leads to adoption of the new without sufficient examination.
The Wave 3 challenge is not to jump straight into the new and exciting, but rather to determine how best to reduce the twin dangers of changing too early, and of moving too late.
The biggest change will require us to ask what changing circumstances and future communities will DEMAND of us, what the new needs will be, and not to look at new technology as merely an opportunity to change the way we SUPPLY the current needs of our customers and community.
From Supply to Demand. In the past most of the information we have needed for our decision making in asset management has been internally generated and recorded in our Asset Information Systems. This has been solely supply side information. We still need our supply side information. But this will not suffice. Knowing what we CAN do is not enough. We need also to look at what we MUST do. For this, we will increasingly require the ability to understand and anticipate future demand change. This is why our our asset management teams will need to expand to include the talents of many other professionals, as I have suggested in the table above.
Is your Asset Management Team prepared?
Is your Asset Management team prepared to tackle the third wave? If you are not sure, then a good place to start would be with “Building an Asset Management Team” by Ruth Wallsgrove and Lou Cripps. This will help you recognise not only requirements but also the many new possibilities. Here is a short excerpt “What kind of people does an AM team require?”
Note: When you buy “Building an Asset Management Team” you not only get the very latest thinking in AM teamwork, but you pave the way for future developments, for Ruth and Lou are donating all their proceeds (ALL, not just profits) to Talking Infrastructure.
So go ahead, click this link to get your copy. You can get a Kindle version for less than $10. In this case value greatly exceeds cost. It’s priced low to maximise the number of teams that can gain access. Spread the word!

I was wrong. Movement from maintenance to asset management, to strategic asset management is NOT a revolution. Why not?
In 2018, for the IPWEA’s online journal, Jeff Roorda and I sketched out what we saw as the general pattern of these individual journeys and what this suggested about where we would go next. At the time there was a lot of discussion about the third (and for some) the fourth industrial revolution. We needed a sexy title for our paper so we called it ‘The third AM Revolution’.
We saw AM moving from the pre-AM stage of maintenance only to the first stage of data collection, or ‘asset inventory’, to the second stage of performance and alignment, or what we call ’Strategic asset management’ – the stage we believe most of Australia is now in – to a new third stage, our ‘third revolution’ that we are calling ‘infrastructure decision support’.
We now see that ‘revolution’ was the wrong word.
Revolutions have connotations of what was previously important getting the chop – quite literally in the French Revolution! Although each of the three stages we identified are still important because they represent different mindsets and approaches, different groups of players and different techniques, they do not discard what went before. Instead they increase our understanding of their value and make them stronger.
Let’s see how that works.
0. Before AM there was maintenance. Maintenance specialists firmly believed in the value of their work, and they were right. Unfortunately they were unable to convince others, especially finance. When AM came along it provided a framework to demonstrate that not only was maintenance able to fix what was currently broken – it could also help prevent more breaking down in the future. That is why so many maintenance engineers were keen to see AM adopted by their organisations.
1. The first stage of AM, naturally, was to establish an asset inventory. We needed to know what we had to manage.
2. With enough basic data we were enabled to take the next step use the data collected for performance improvement. When we did this, we became much more aware of data quality and coverage. That first stage of data collection did not get the chop, now we wanted more. Instead of data being required simply for a mandated balance sheet (e.g. a storage location) it was increasingly seen as necessary, indeed essential for progress, and so demand for more data, and for data of a higher quality with greater coverage has continued.
3. The coming third stage is what will bring all of these stages – maintenance, data collection and performance improvement or strategic asset management – together, for it is at this third stage that asset managers finally reach the stage that they have desired for a long time. Asset management is able to get (and worth a) place at the board table!
So not a revolution. But what?
We could simply call them ‘three stages’ and be done with it. This, however, would not show the connection between them, how each builds on what went previously, so we are calling them waves, for like waves they build on each other and get stronger.
Why is this important?
Because now that it is so easy to access detailed information about the second wave of strategic asset management or performance improvement (IIMM, PAS55, ISO 55,000) there is a temptation is to dive in at this level. But without attention to the first wave of data collection and without strengthening the pre-AM stage of maintenance, such attempts lead to failure. Under-developed countries wanting, and needing, to do fast catch up with the developed world are at particular risk.
They are being pressured ‘to do asset management’ in order to get the strategic asset management, second wave, benefits but the importance of funding and training at the earlier stages, particularly maintenance is not being recognised and dealt with. Every stage – maintenance/pre-AM, data collection/asset inventory, and strategic asset management/performance improvement or alignment – requires a different focus, different tools, different groups of players.
I will talk about Wave 3 – where we go next – in a later post.
Q: Does this development pattern make sense to you?
Can you recognise it in your own organisation or others? Is it obvious, or do you see an alternative pattern to your own asset management journey?

Recent Comments