 This is a brief account of a lengthy 2014 dialogue I had with Patrick Whelan, a thoughtful architect in WA. You are now invited to join the discussion.
This is a brief account of a lengthy 2014 dialogue I had with Patrick Whelan, a thoughtful architect in WA. You are now invited to join the discussion.
Patrick: In WA, a scoring model was devised and adopted for all police buildings, It scored building fabric condition and the condition of services to determine an overall condition score. The building’s suitability for purpose was then determined by comparing scores for compliance with the Building Code of Australia and for compliance with the Police Building Code (the agency’s accommodation standards) Comparing the Condition score with the Suitability score enabled a ‘works priority score’ for the station, in effect displaying a level of service offered by each station.
Penny: Whilst building condition and code compliance are important, they are important from the perspective of the building maintenance manager. To get at the idea of service perhaps we need to look at what the building user wants to get out of the building. A building may be in excellent condition and meet all code conditions, yet still fail to work efficiently for the user. It may be that the design is no longer suitable for the new work that needs to be carried out, or it may have the wrong capacity – either too much or too little. It may be in the wrong place!
Patrick: In the case of the WA Police, their Building Code articulates everything needed of a building to progress policing: Planning criteria, technical criteria, functional relationship diagrams, room data sheets, formulae for calculating room sizes and the number of ablutions facilities, guidelines for the compliant design of custodial facilities, etc. The Police, being a paramilitary organisation, have a very strong handle on what is needed to do the job. However, things change over time, and the building code changes with them.
Penny: Building codes are so efficient because, in the short term, people only need to respond, ‘on the dotted line’, as it were: they don’t have to think. However can what makes for short term efficiency lend itself to longer term ineffectiveness? What can be done to determine a code that is both efficient and effective?
Over to you!
 We all know early option analysis makes sense so why don’t we do it?
We all know early option analysis makes sense so why don’t we do it?
Maybe there is a desire to ‘get runs on the board’, to be able to show the media, as well as government sponsors and promoters, that ‘something is happening’ and that the team assigned to the task are not dragging their feet. While a project is in the early options appraisal phase it requires a lot of flexibility – and time – from senior executives, who are the only ones who can determine when sufficient evidence is presented to enable a choice to be made as to the direction to be taken. Once the direction is chosen the work can be passed to lower levels or consultants to construct the ‘business case’. Experience with the Victorian Investment Logic Mapping work confirms the difficulty of getting senior executives to spend the necessary time on this high level decision making.
Danger of default to ‘the infrastructure solution’
In 2000, according to the UK Institute’s Report “What’s Wrong with Infrastruture Decision Making”, there was an analysis of the environmental impact of intermittent discharges of storm sewage into the Thames. They concluded that “The main problem with the early options analysis was that a mixed solution (using a combination of smaller measures to address storm sewage) was not considered in detail . This is an example of the seeming preference within government for large projects.”
The tunnel, now under construction, has a total cost of £4.2bn and will add an estimated £15-25 a year to London water bills until 2023/30. Critics say that the cost is unnecessarily high and that cheaper alternatives were never explored properly. The Institute argues that decision makers on the project may have fallen prey to perceived political risks, staff fears of expressing disagreement and decision-making processes sceptical of innovation, which made decision makers reluctant to turn back after making an early commitment.
So our inquiry today is:
-
Why don’t we do, what commonsense says we should?
-
What experiences have you had that illustrate a too quick default to the infrastructure option.
-
And what can we do about it?
 DeBono invented the term ‘Po’ for a provocation – something that begged to be thought about and commented on!
DeBono invented the term ‘Po’ for a provocation – something that begged to be thought about and commented on!
In this light, my friend, Miso, has submitted the following:
“With respect to managing infrastructure, the shortcut to “a more enjoyable trip” is to say that rather than expanding resources on collecting more condition data, let’s “recycle” (actually use for the first time) the mountains of information we have produced through decades of decision making.
By analyzing patterns in financial, engineering, and administrative data we can derive the comprehensive infrastructure performance measure. One which inherently accounts for all factors (e.g. conditional and functional) which were taken into account when the professionals made their decisions.”
Your Thoughts?
18 months ago I had the pleasure of co-designing and presenting a capacity building workshop for Auditors-General in the Pacific Islands. The subject of the workshop was auditing for the better management of public assets. We looked at the 4 stages – planning, construction,operations & maintenance and, finally, renewal or disposal – and discussion revealed that the auditors chose to spend the bulk of their time in analysing performance at the operations & maintenance stage. This made sense. It is by far and away the area where most expenses occur. However, it is not the stage where most expenses are committed. That occurs much earlier, at the planning stage. This is the stage where the nature, location and size of the project are determined and these are the primary determinants of how much will be spent later at the operations and maintenance stage.
I drew up a hypothetical schema to make the point. It showed that, by the end of the first or planning stage, only $4m of the total life cycle costs ($203m) had been spent BUT, the decisions made during this phase had already committed about 75% (and sometimes more) of the total costs. In the diagram the green line represents costs actually expended, the blue line costs pre-determined and the purple line represents the scope remaining to make a difference to total costs. This shows that by the time the plant is commissioned and operational, there is really relatively little that can then be done to improve on the overall life cycle costs.
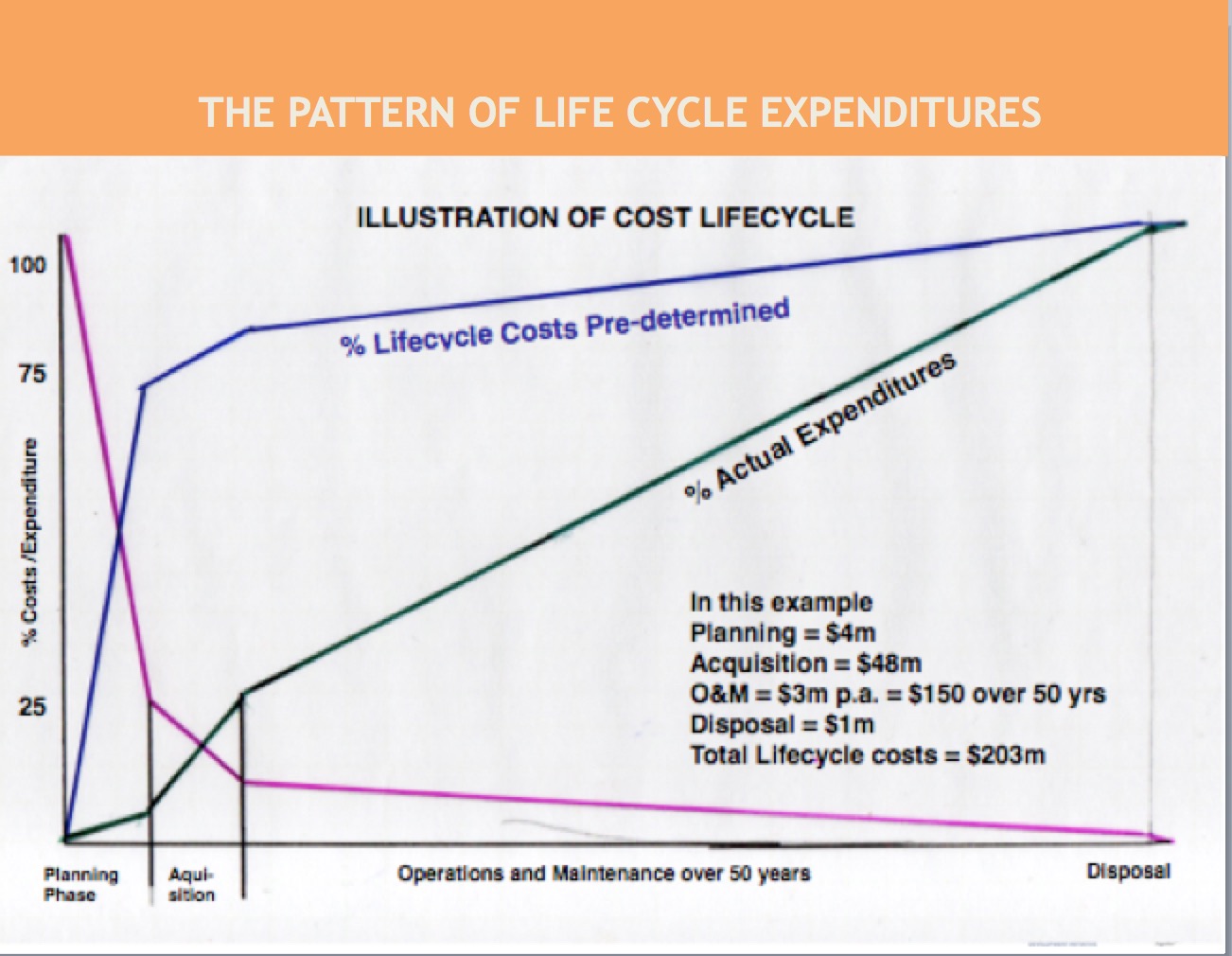
The figures I used in this example are fictitious.
They are consistent with the theory and principles of life cycle costing as shown in the major textbooks on the subject.
I would have liked to use real figures but I couldn’t find any. So I contacted people who might be expected to know – key academic figures in asset management, experienced consultants, long time practitioners. But no, no-one could help.
So my question today is:
Why do we have so little actual data about this very key and critical stage of decision making? And how can we improve our knowledge – and thus our performance?

In the last post “The Infrastructure Quiz” I asked what the ‘purpose’ of infrastructure is. What did you choose? If you ask this question of most people, the answer is obvious – it just isn’t the same answer for everyone!
Have a look at the following possibilities:
- For asset managers, the answer is obvious – it is to provide needed services that underpin the economy and society well being.
- For economists in the Treasuries, the answer is equally obvious – it is to kickstart the economy. (For many years we had a stop-go policy for infrastructure. Whenever the economy got overheated, governments would cut back on infrastructure spending, and whenever it slowed down, they would spend more. There was a period in the early 2000s when this was recognised for the damage it caused. But now it seems to be back again.)
- Politicians and Think tanks are the ones likely to claim that infrastructure – ‘increases productivity’ and ‘raises the standard of living’ (but they seldom spell out exactly how, for it is all regarded as self-evident.)
- For the general public (most of whom could not give any examples of infrastructure beyond roads, if that) the answer is that the purpose of infrastructure spending is to ‘create jobs’.
- Military and strategic planners often see the construction and location of infrastructure as a strategic control problem. Many politicians do the same.
- The construction industry and its lobbyists strongly believe that we not only need infrastructure to keep the industry afloat but that we need to forecast what infrastructure and where in order to enable them to plan.
So, many purposes – all ‘self evident’!
 The UK Government has been criticised for its lack of a national infrastructure policy. Some might say this applies to Australia as well. However, before we can develop an infrastructure strategy that can gain national acceptance, we need to have a general understanding across the nation about the purpose of infrastructure. In other words, common agreement on ‘what’s it for?” So, today, we have a little quiz.
The UK Government has been criticised for its lack of a national infrastructure policy. Some might say this applies to Australia as well. However, before we can develop an infrastructure strategy that can gain national acceptance, we need to have a general understanding across the nation about the purpose of infrastructure. In other words, common agreement on ‘what’s it for?” So, today, we have a little quiz.
1. Which of the following BEST expresses for you the prime purpose of infrastructure?
- create jobs
- increase productivity
- maintain strategic control
- provide a needed service
- raise the standard of living
- stimulate the economy
- sustain the construction industry
- SOMETHING ELSE (please describe)
2. Do others see things the same way? Spend a few minutes and consider who might support each of the other definitions. (Research shows that each idea IS supported by some group.)
3. For those within an organisation, does your organisation see things the way you do? What is the evidence that they do? E.g. A policy, a principle, or, better yet, a practice.
4. Looking now to the State or the Federal level of government, what purpose would you say most reflects their infrastructure choices? Are their choices consistent with each other? Is what drives them also what drives you or your organisation? That is. do you have the same purpose? How do you know?
Have fun!
And do click the ‘add a comment’ tag in the menu bar and share any of your ideas.
 Roads are a major asset, probably the major asset, of every council, so ‘doing different’ here can make a real impact. So, following on from our earlier post (Feb 6) by Rebecca Brown, here is another angle on road recyling, this time by Con Rimpass, Pavement Analysis, who looks at not just partial use but 100% recycling of roads with cold asphalt, improving on the ‘cradle to grave’ notion, by extending it to perpetual life! Both authors are presenting their work at the 2018 IPWEA State Conference, Perth, March 21st to 23rd.
Roads are a major asset, probably the major asset, of every council, so ‘doing different’ here can make a real impact. So, following on from our earlier post (Feb 6) by Rebecca Brown, here is another angle on road recyling, this time by Con Rimpass, Pavement Analysis, who looks at not just partial use but 100% recycling of roads with cold asphalt, improving on the ‘cradle to grave’ notion, by extending it to perpetual life! Both authors are presenting their work at the 2018 IPWEA State Conference, Perth, March 21st to 23rd.
Con says: There is nothing new about cold mixed recycled asphalts, they have been around, particularl in France, since the mid 1970s and known as cold mix asphalt & grave-emulsion and they have been manufactured from either new or recycled material or a combination. Cold mixed asphalt and bitumen stabilisation are used in the renewal of both pavement structures (bases) as well as for surface wearing courses and have proven economic, environmental and safety benefits.
As Perth has grown in population so too has its length of roads and these aging roads now have to withstand heavier traffic with large loads on high tech tyres pumped to very high pressures, creating a huge increase in strain on the pavement structure. Perth has a network of road pavements that have had two or more asphalt overlays without any structural improvement to support layers and there is evidence that some money is being wasted on rehabilitations that are not providing satisfactory lives.
It is not possible, or economical, to continue to just resurface road pavements for ever without stiffening the support and it is important to try and recycle as much of the existing pavement materials as possible. The government is aware of this and are encouraging the use of recycled materials.
Asphaltech, in partnership with Pavement Analysis and collaboration and support from French experts have developed a process which makes it possible to 100% recycle and strengthen pavements with minimal disruption to traffic and exposure of workers to the safety aspects of working on live roads.
For those unable to hear Con at the conference, please enter your questions in the comments section (click the ‘add a comment’ tag in the menu above) and he will be happy to respond.
 Thought for the day
Thought for the day
‘Well chosen infrastructure projects contribute to job creation and increased productivity’.
Notice anything odd about this? (Apart from the fact that it is a circular statement, since ‘well chosen’ is presumably defined by the outcomes achieved.)
Increasing Productivity
When we ‘increase productivity’ we enable the labour force to produce more. This is normally done through investment in capital, and nowadays through increasing use of automation. When we are struggling to produce enough to meet demand, that is, in times of low unemployment and high demand pressure, increasing productivity leads to an easing in the economy, reducing inflationary pressures. It is good.
However, in times of low demand – i.e. when we have high unemployment – increasing the ability of firms to produce more with less, may increase profits, but if there is not the demand in the economy to soak up this increased output, this is at the expense of reducing their need for labour. Then, it is not so good, at least not for labour. And, to the extent it is successful, increases the demand for job creation.
Job Creation
When do we wish to ‘create jobs’ – in times of high, or low, unemployment? Clearly in times of high unemployment. In other words, precisely at the time when ‘increasing productivity’ will lead to less job creation’.
‘Job creation’ and ‘increased productivity’ would thus seem to be incompatible goals for Government. And hardly justification for expensive investment in infrastructure. There must be a better argument.
Thoughts?

This is by way of a ‘heads up’ to coming posts on infrastructure decision making. In June last year, the Institute for Government in the UK produced the report “What’s wrong with infrastructure decision making: conclusions from six UK case studies”
Major conclusions were:
- There is no national strategy for infrastructure investment
- Government does not devote enough time to assessing early options and seizes apon preferred projects too soon
- The more ambitious the project, the more questionable the model
- A failure to understand project risk
- The difficulty of making decisions which create ‘concentrated losers’ (which can and do become vocal opposition groups)
- Inadequate post project evaluation means we do not learn for future projects
You can probably identify with all of these problems in your own work. The Institute draws on mega projects in the UK such as The Third Heathrow Runway, the High Speed 1 and 2 rail proposals and the ultra expensive Hinkley Point C nuclear energy plant proposal, amongst others. But you can think of large and small projects in your organisation, state or country.
Over the next six posts we will consider each of these and then look more closely at the way we make our infrastructure decisions here in Australia. We are all familiar with studies that argue that government decision making is abysmal and should be replaced with private sector decision making, which is assumed to be so much better ‘because it is focussed on profit making’. But when it comes to infrastructure, both economic and social infrastructure, ‘profit-making’ is not the goal. Here, we are really looking at ‘the social value of shared resources’ in the terms of Brett Frischmann.
It is important to bear this in mind as we consider these infrastructure decision making problems, no matter who is making them, for when an infrastructure decision is passed to the private sector to make, it is a public sector decision that makes this possible.
QUESTION: What other problems beside these can you identify?
 The 9th World Urban Forum was held in Kuala Lumpur a week ago. This is where tens of thousands of people from across the world gather to find ‘best practice’ examples and ideas that they can take back to their countries or organisations to improve their communities. Now, apart from being different from what is being done now, what commends a particular ‘best practice’ example to any individual participant? What should? What do you look for in a ‘best practice’ example? (e.g. what tells you that it IS ‘best practice’?) What would it take to develop a guidance tool to quickly assess any given example, to enable you to hone in on those with the most opportunity for success? Considering the dangers of ‘doing different’ just for difference sake, of which we spoke in the last post, I have, over the last few months, been speaking with a couple of colleagues as to how this could be done.
The 9th World Urban Forum was held in Kuala Lumpur a week ago. This is where tens of thousands of people from across the world gather to find ‘best practice’ examples and ideas that they can take back to their countries or organisations to improve their communities. Now, apart from being different from what is being done now, what commends a particular ‘best practice’ example to any individual participant? What should? What do you look for in a ‘best practice’ example? (e.g. what tells you that it IS ‘best practice’?) What would it take to develop a guidance tool to quickly assess any given example, to enable you to hone in on those with the most opportunity for success? Considering the dangers of ‘doing different’ just for difference sake, of which we spoke in the last post, I have, over the last few months, been speaking with a couple of colleagues as to how this could be done.
Where do we start? Firstly – Know thyself! Those of you who were caught up in the benchmarking craze some years ago, may remember how organisations would gleefully arrange meetings with ‘best practice’ organisations to see what they could glean. And they would do this, without first taking the trouble to understand fully what they were themselves doing. Many changes were made that lacked understanding, and caused more damage than they avoided.
A first iteration of such a guidance app, with a strong focus on understanding our own organisations and what is driving their decision making, was trialled at the Urban Forum in KL last week which established proof of concept.
We are now considering a forum for further development and testing.
Question:
Does this idea intrigue you? And would you would like to be part of its further development? If so, please let me know in the comments section below or write me at penny@TalkingInfrastructure.com
Next Week: Problems with Infrastructure Decision Making.

Recent Comments